Published Sep 04, 2023 by Xiph
Open-source intelligence (OSINT) has emerged as a vital tool for cyber security. It’s used by businesses, governments, and other organisations alike to gather cyber intelligence from publicly available and legally accessible sources.

What is open-source intelligence (OSINT)?
Open-source intelligence involves collecting, analysing, and interpreting data from publicly available sources on the internet to obtain valuable insights. These sources include social media platforms (e.g. Facebook, Instagram, Twitter/X), websites, blogs, forums, news articles, and any other publicly accessible information on the internet. The aim of OSINT is to gather relevant data that can be used to understand, assess, and mitigate potential security threats and cyber attacks.
Unlike classified or confidential data that requires special access, OSINT relies on information that is freely available to anyone with an internet connection. This makes it a valuable tool for cyber security professionals, but also for law enforcement authorities, researchers, journalists, and businesses seeking competitive intelligence.
How does open-source intelligence (OSINT) work?
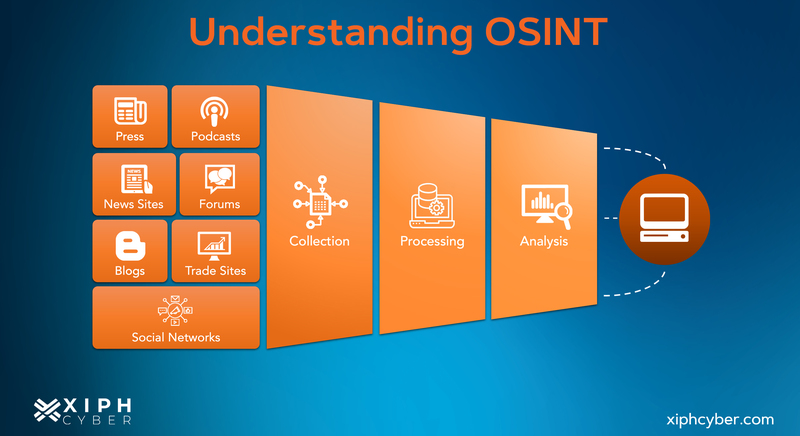
Here's a general overview of how OSINT operates in the field of cyber security:
-
Data collection: The first step in OSINT is identifying and collecting relevant data from all publicly available sources online. This can involve manual searches on search engines, social media, government or commercial databases, public libraries, academic papers or using automated specialised OSINT tools and software to do it for you.
-
Data analysis: Once the data is collected, it must be processed to remove duplicate, irrelevant or inaccurate data and to extract meaningful insights for your cyber security strategy. Particularly patterns, trends, connections, and anomalies within the data and the information subset you want to investigate.
-
Data interpretation: After analysis, the information is interpreted to draw conclusions and make informed decisions. This step often requires a deep understanding of the context and domain knowledge.
-
Reporting: The final insights are compiled into a comprehensive report, which can include actionable recommendations based on the findings. Cyber security teams can use this report to develop their response plan and countermeasures.
Open-source data examples
Images and videos posted online: Analysing visual content can reveal individuals' locations, objects, and identities. Techniques like reverse image searches can verify authenticity and identify original sources. Metadata extraction provides valuable insights, while geolocation tools can pinpoint where a certain image or video was created.
Social media posts: Information shared on social media platforms like Facebook and Instagram can provide insights into people’s online behaviours, interests, and affiliations.
Public databases: Various online databases, such as public records, government websites, and academic repositories, can contain valuable information about individuals, organisations, and events. Some well-known cyber security databases in Australia include CERT Australia and the Office of the Australian Information Commissioner (OAIC).
Online forums: Discussions on forums and community platforms can reveal trends, opinions, and potential threats within specific interest groups. Some popular platforms to monitor for cyber security include Reddit, Discord, Quora, Hive and other community forums or open-source systems.
Dark web: Focus on threat intelligence, stolen data markets, hacking forums, and trends in cyber crime. Be aware of misinformation, understand the challenges of dynamic, hidden websites, and ensure you’re still complying with legal and ethical standards.
Company websites: Company websites often provide information about their employees, technologies, and business strategies that can be useful for competitive intelligence.
News articles and blogs: News articles and blogs can offer insights into current events, emerging threats, and trends in the cyber security landscape.
How is open-source intelligence used?
Threat detection and prevention: OSINT is crucial in identifying potential threats to an organisation's digital infrastructure. By monitoring online conversations and activities, cyber security professionals can detect early signs of cyber attacks and take proactive measures to prevent them. For example, you could monitor dark web forums and social media for discussions about potential zero-day vulnerabilities in specific software or applications.
Vulnerability assessment: OSINT can help identify vulnerabilities within an organisation's network and systems. It can help uncover weak points that malicious actors could exploit. For example, you could use OSINT tools to search for public information about an organisation’s network infrastructure to revise security configurations and restrict access.
Phishing and social engineering: Cyber criminals often use social engineering techniques to deceive individuals into divulging sensitive information. OSINT can help in understanding attackers' tactics and devising countermeasures.
Investigations and digital forensics: Cyber security professionals can use OSINT to gather evidence, trace online activities, and reconstruct digital trails to solve cyber crimes and prevent future attacks.
Brand protection: OSINT can assist businesses in monitoring online mentions and discussions related to their brand. This helps in identifying instances of fraud, counterfeiting, or reputation damage.
Incident response: During a cyber security incident, OSINT can provide real-time information about the nature and scope of the attack. This information is invaluable for formulating an effective incident response strategy. For example, if your business becomes the victim of a ransomware attack, it could use OSINT sources to determine the ransomware variant, its capabilities, and the attacker's demands. This information would then guide their response strategy.
OSINT ethical and privacy considerations
While OSINT provides numerous benefits, it raises important ethical and privacy concerns. The information collected might include personal data, and its misuse can lead to privacy violations, identify theft and other crimes. Therefore, conducting OSINT within legal and ethical boundaries is essential, as well as respecting individual privacy rights and adhering to industry regulations.
A final word
Open-source intelligence is a valuable tool in the cyber security arsenal and provides a more holistic approach to threat detection, vulnerability assessment, and incident response. By harnessing the power of publicly available information, businesses and organisations can get valuable insights that help further protect their digital assets. For more information on OSINT best practices, contact us via email: enquiries@xiphcyber.com.
Posted in: Security


