Published Mar 27, 2022 by Xiph
Did you know that 78% of the most popular passwords in Australia can be cracked within seconds?

Weak passwords and login credentials can put your personal data and financial information at risk, or worse, lead to hackers blocking access to your devices and applications. The careless use of passwords can have even more devastating consequences for businesses and organisations, including the undermining of IT assets and security protocols, data exploitation, loss of confidentiality, and bankruptcy.
That’s why robust password protection is so important – it’s the first line of defence against cyber intrusion.
What is password protection?
Passwords or password protection is arguably the common form of authentication. It’s often the only barrier between you and your personal information. Password protection allows only those with an authorised password or login to gain access to certain information, applications, or devices. Therefore, the stronger your password is, the more protected you are from hackers and malware.
Why is password protection important?
Australia was classified as ‘high risk’ of data leaks, according to NordVPN. Having a robust and secure password is the first line of defence to protect data sets, personal and commercial information, files, applications, software, and devices from being hacked or lost. In this day and age, hackers and other cyber criminals are becoming more ingenious and continuously find new ways to exploit our security vulnerabilities for financial gain.
How to create a strong password
Here are some basic best practice rules to follow to create a secure password:
- Create a password that is between six and 12 characters long
- Use a varied combination of upper and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols
- Check your password health to identify any weaknesses in your passcode
- Use different passwords for different accounts and devices
- Don’t re-use passwords, even if it’s been years since last used
- Steer clear from default passwords or passwords that include a family name, date of birth, or address
- Never disclose your passwords to others
- Never provide passwords or login credentials requested via email
- Change your password every three to six months
- Use a multi-factor authentication
- Use a password manager
How often should you change your passwords?
Security and IT experts recommend changing your passwords and login credentials every 90 days, depending on what the password is used for (account, file, application, device, etc.), how frequently it’s used, and how strong the password is more broadly. However, make sure to change your password immediately if you think it’s been compromised in any way.
Should you use a password manager?
Crafting and remembering complex passwords for all your accounts and devices is a recipe for insanity. So, yes, it’s a good idea to use a password manager to keep all your passwords secure in one place and without having to memorise them all. Think of a password manager as like a virtual vault for all your login credentials. Password managers also help generate robust passwords for sites you visit and automatically fill in your login name and password each time you jump on your favourite websites. Both individuals and businesses use password managers to securely store and manage all of their login credentials.
Top 7 best password managers for 2022
Here are some of the best and most widely used password managers online.
-
Bitwarden
- Unlimited passwords & form filling in free version
- Secure password generator
- Two-factor authentication & biometric login
- Available for Windows, Mac, iOS, Android, Linux
-
LastPass
- Feature-rich free version (including form filling)
- Syncs among same devices
- Two-factor authentication & biometric login
- Available for Windows, Mac, iOS, Android, Linux, Chrome OS
-
Dashlane
- Built-in VPN & dark web monitoring
- Easy syncing between devices
- Two-factor authentication & biometric login
- Available for Windows, Mac, iOS, Android, Linux, Chrome OS
-
1Password
- Travel mode & web scanner
- 14-day free trial
- Two-factor authentication & biometric login
- Available for Windows, Mac, iOS, Android, Linux, Chrome OS, Darwin, FreeBSD, OpenBSD
-
Keeper
- Secure password sharing & inheritance
- Full password & file history
- Two-factor authentication & biometric login
- Available for Windows, Mac, iOS, Android, Linux, Chrome OS
-
NordPass
- Feature-rich free version
- Auto-fill with passwords, credit cards & secure notes
- Two-factor authentication & biometric login
- Available for Windows, Mac, iOS, Android, Linux, Chrome OS (web vault only)
-
RememBear
- Game-like interface & feature-rich free version
- Easy master password recovery
- Two-factor authentication & biometric login
- Available for Windows, Mac, iOS, Android
Should you use multi-factor authentication?
Yes! Two-factor authentication (2FA), or multi-factor authentication (MFA) is the single most effective security tool to prevent unauthorised access to online accounts. In fact, an MFA can block 99% of account breaches or attacks online, according to a study conducted by Microsoft.
Using a 2FA or MFA to authenticate users is now also a mandatory requirement for many online platforms. This includes most customer relationship management (CRM) software, trading platforms, banking apps, and even social media platforms like Facebook. Using an MFA also helps to secure password manager accounts and mitigate the risk of a breach.
.jpg)
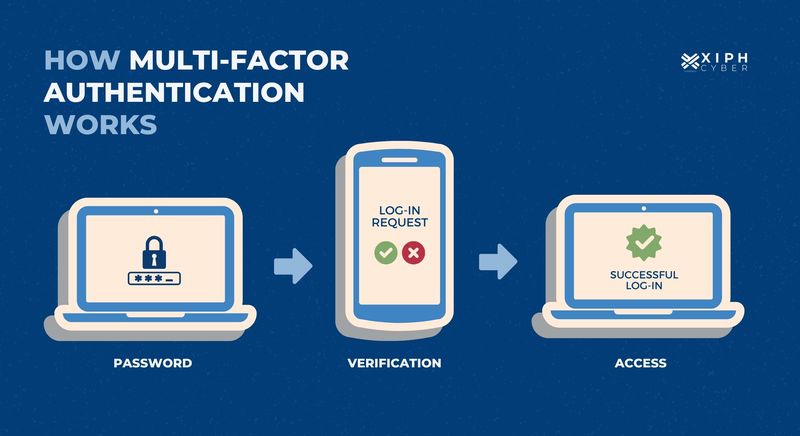
What is multi-factor authentication?
MFA or two-way authentication is a security technology used to authenticate the identity of a user. Traditionally this involved confirming your username and password, but multi-factor authentication adds another layer of security and requires users to provide two or more pieces of evidence (called factors) to verify their identity to gain access to an app or online platform. Typically, each proof of identity must come from one of three different categories:
- Something you know (i.e. password or PIN)
- Something you have (i.e. your smartphone or a secure USB hub)
- Something you are (your fingerprint, or facial recognition)
Can a password be hacked?
Passwords aren’t fail-safe and can definitely be hacked. Most passwords are stored in secure systems that use special hashing or cryptographic algorithms to keep your information safe. However, hackers can still crack your passwords using different techniques like ‘dictionary attacks’, ‘password spraying’ and ‘brute force attacks’. That’s why strong password protection, coupled with MFA is key to keeping your online accounts safe.
A final word
Without proper password protection, it’s far easier to fall victim to cybercrime and identity theft; each of which can have devastating impacts on both individuals and businesses. For advice or information on the best password managers and multi-factor authentication systems, contact us via email: enquiries@xiphcyber.com.
Posted in: Security


