Published Jun 03, 2022 by Xiph
Chances are you’ve used ‘the cloud’ before – when you’ve been on Instagram, YouTube, or even Gmail − (yes, they all use cloud computing). Although the majority of internet users and businesses use storage space on the internet, cloud storage and how it works is still a mystery for many. Fret not, we cover all the fast facts in this guide.s and photos in the cloud, while businesses use cloud storage for data backup, disaster recovery, archiving, and DevOps projects.

What is cloud storage?
An alternative to storing data on-premises, cloud storage is a cloud computing model that allows individuals and businesses to save, manage and access their data securely and exclusively online. This means it can be accessed anytime from any location and easily shared on any device with an internet connection. Data and files stored in the cloud get sent to remote servers in a physical location typically owned and managed by a cloud service provider. Cloud storage also offers a way to back up data to facilitate recovery off-site. Cloud data storage is usually paid for as a monthly subscription fee based on the amount of storage used. Most individuals have probably used services like Dropbox, Google Drive, or One Drive to store documents and photos in the cloud, while businesses use cloud storage for data backup, disaster recovery, archiving, and DevOps projects.
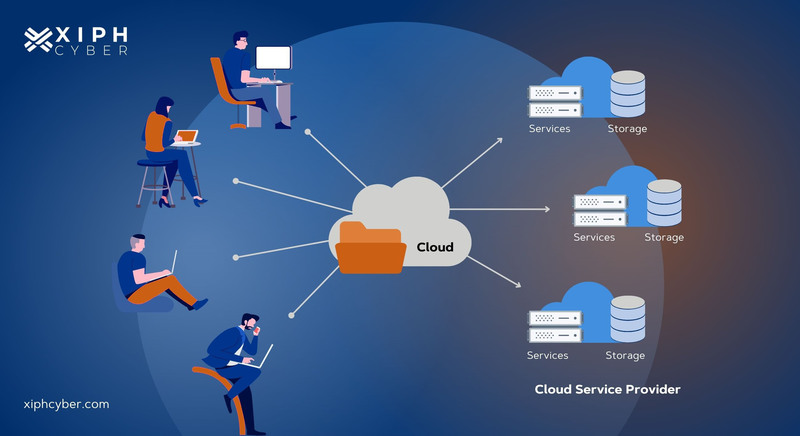
How does cloud storage work?
Cloud storage stores and retrieves your data from a little corner on the internet owned by you. Like local on-premise storage networks, cloud storage uses physical servers to save data – but instead of being on-site, your said data is sent to virtual machines hosted on a physical server at an off-site location. Your data is not stored on any local hard drive, but you can access and control it remotely via web interfaces. As your storage needs increase, your cloud service provider creates new virtual servers to accommodate your storage needs.
It works a little like this:
- You send your data/files securely online to a data server (maintained by a cloud service provider)
- The data server with which you connect forwards the information to a pool of servers
- You can remotely access your data/files anytime through a web-based interface
Cloud storage totally eliminates the need to own or manage your own data storage infrastructure. You can store all types of information in the cloud including archives, financial information, client files, databases, images, videos, and more.
Where does your data go?
Contrary to what some people believe, data you upload or run on the cloud isn’t floating around in cyberspace. It gets sent to individual servers in data centres (otherwise known as server farms or warehouses) located all over the world. These data centres and warehouses are owned by cloud service providers, who are responsible for keeping the servers up and running at all costs. Cloud service providers are also responsible for keeping your data safe from theft and ensuring it’s available to you anytime you want it. Many companies outsource their server farms to satellite locations in order to reduce costs, so this in turn makes it difficult to know where your data actually resides, and the cloud provider may not necessarily disclose this information for obvious reasons.
Cloud storage vs local storage: What’s best for businesses?
Traditional on-site storage solutions like hard drives can be inconsistent in their cost, performance, and scalability, which is why cloud storage should be a no-brainer for any business. Big data projects demand large-scale, affordable, easily accessible, and secure storage. Many businesses also use cloud computing as a backup solution in case of a hard drive failure or other hardware malfunction.
Cloud storage is also safer than local storage overall. Cloud storage providers have airtight disaster recovery plans and backup strategies to ensure that your data is never lost, in addition to offering security services including encryption, password protection, and multi-factor authentication (MFA). Cloud storage providers use sophisticated encryption algorithms to ensure only authorised personnel and employees have access to your documents and files stored in the cloud.
Types of cloud storage
Cloud storage is basically the online storage of data, but not all cloud storage is created equal. Here are the three main types of cloud storage:
Private cloud storage: It’s internal cloud storage that keeps your data stored on the company or organisation’s intranet and that is protected by that enterprise’s own firewall. Private cloud storage gives the user complete control and security customisation, although this will include being in charge of its maintenance and updates. Companies may choose to take full control of an on-premise private cloud or engage a cloud storage provider to build a dedicated private cloud accessible with a private connection. Private cloud storage is a great option for companies that deal with sensitive or financial data like banks, healthcare providers, law enforcement agencies, etc.
Public cloud storage: With public cloud storage, the user or company doesn’t need to maintain the system. Instead, you connect over the internet to a storage cloud that’s maintained by a cloud provider used by other companies. Public cloud storage requires fewer administrative controls and can be accessed online by the user/company and any authorised parties. The main downside is that there’s limited opportunity for customising security fields. Some popular public cloud storage service providers include Google Cloud, Dropbox, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and IBM.
Hybrid cloud storage: This is a combination of private and public cloud storage and gives companies and organisations a choice of which data to store in which cloud. For example, highly sensitive or regulated data could be stored in a private cloud environment, while less sensitive data (such as emails and photos) can be stored in the public cloud.
Cloud storage: Pros & cons
Cloud-based storage offers some distinct advantages over traditional on-premise storage systems, but there are also some disadvantages worth keeping in mind, especially around security concerns and administrative control.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Off-site management – the cloud provider manages and protects your stored data which eliminates the need for your business to own data storage infrastructure. | Security – public cloud storage is shared among multiple parties, which multiplies your security risks, such as unauthorised access to your data. |
| Affordable – pay a monthly subscription fee or per consumption rate. | Latency − delays in data transmission to and from the cloud can occur on shared public internet connections. |
| Scalable – your cloud service provider can create new virtual servers on demand to accommodate data increases. | Limited administrative control – public cloud platforms store and manage your data which can limit control over own your information. You can mitigate this risk by using private cloud storage for sensitive data. |
| Data backup − the cloud protects data from physical disruption like a natural disaster, power outage, or cyber attack. | Not a universal solution – data privacy and archival requirements in some highly regulated industries (i.e. health, finance, etc.) may prevent the use of cloud storage for certain files/data. |
Is cloud storage safe?
Most enterprises use more than one cloud storage solution, so it’s safe to say it’s perfectly secure and safe to use provided you’ve got a comprehensive cloud storage plan to mitigate risks of misconfigurations or data losses. Cloud storage is designed from the ground up for maximum data security. All data files in the cloud are encrypted and locked away to ward off cyber criminals. What’s more, data in the cloud is stored redundantly to ensure that your information always exists somewhere and survives in any event. Cloud providers also continuously employ various security measures to protect your data, including built-in firewalls, third-party security testing, artificial intelligence (AI) and auto-patching, and backups, just to name a few.
A final word
The availability, durability, and cost benefits of cloud storage don’t always outweigh security concerns around data integrity and compliance for some businesses, so it’s best to speak to cyber security experts about which cloud storage solution(s) best fit your needs. For more information, contact us via email: enquiries@xiphcyber.com.
Posted in: Security