Published Sep 15, 2022 by Xiph
System breaches and data loss can happen to any business − big or small − either due to accidents of human error or hardware failure or because of more sinister events like malicious software or ransomware. That’s where having a robust data backup plan comes in. Below, we cover everything you need to know about data backups and disaster recovery to future-proof your operations, protect your employees and clients, and safeguard your brand’s reputation.

What’s backup data?
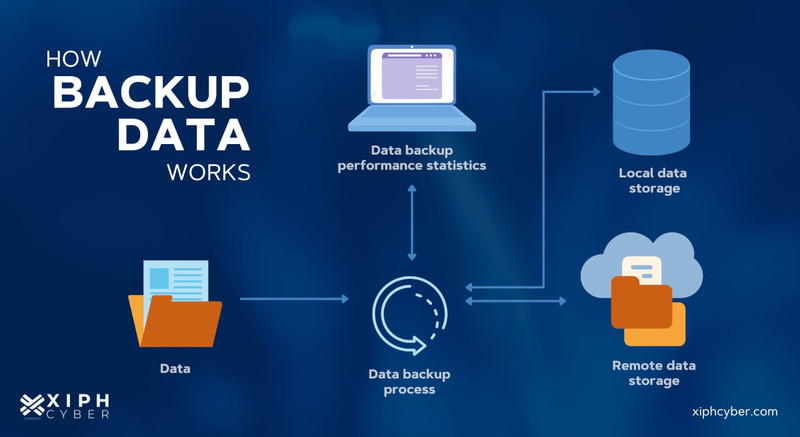
Backup data is synonymous with data protection, and it’s the simple process of creating a copy of your important personal or business information, and operating systems in case the original data is lost or corrupted. You can also use a backup to recover copies of older files (i.e. photos, videos, etc.) you’ve deleted from your systems or devices like computers, smartphones, and tablets. Data losses can occur as a result of hardware failure, breakage, theft, or malware infection like ransomware, human error, or even physical theft or natural disasters (if data is stored locally). Backup data is typically stored in a secure, separate location from an original device, more likely in a cloud environment.
Why is backup data important?
Data security is an essential part of business continuity. In fact, one study showed that 96% of companies with a trusted backup and disaster recovery plan were able to survive ransomware attacks and fully recover their operations. On the flip side, 40-60% of small businesses that lost access to operational systems and data without a disaster recovery plan never recovered and subsequently folded.
It goes without saying − data loss events can cripple businesses operationally, and financially, especially in the event of a ransomware attack whereby organisations may spend millions trying to recover data from bad actors and setting up lost systems. Any data loss, especially of client and customer data, would also damage an organisation’s credibility and even potentially lend them in hot waters legally for breach of privacy.
That’s why all businesses and organisations should have a secure archive of all business-critical information to main their essential functions and operations in the event of a data loss or ransomware attack. This should always include backups of classified documents and internal records such as customer data, employee data, and systems data; all of which are critical for disaster recovery. Businesses should use a combination of on-site and cloud storage for their data. It’s important not to rely solely on local storage to mitigate the risks of theft and natural disasters like storms, earthquakes, fires, and so on. Having a clear and airtight data backup strategy should be part of any business’ cyber security plan.
Read more: SSD vs HDD: Which is better?
What data should businesses back up?
As a general rule, businesses should back up any information and data that can’t be replaced if lost/stolen or that’s critical to business operations. This may include:
- Customer databases
- Tax and financial records
- Invoicing, billing, receivables & payables
- Insurance policies
- Leases
- Patents
- Payroll information
- Employee records
- Configuration files
- Operating systems
- SaaS applications
- Accounting files
- Emails
- Registry files & internal files
- Spreadsheets
Most medium to large-sized businesses will have an IT department to manage backups, ensuring they’re scheduled frequently, working correctly, and secure at all times. On the other hand, smaller businesses may use backup software applications to reduce the complexity of performing backup and recovery operations, or may simply outsource their backup management to third parties or specialised business data backup providers.
Type of backups
There are mainly three types of backups − full backups, differential backups, and incremental backups.
- Full backup: This is the most basic and complete type of backup. As the name implies, this type of backup makes a copy of all data including emails, folders, files, SaaS applications, and hard drives. The primary advantage to performing a full backup is that all data is recoverable within a single set of media, making recovery time minimal. The disadvantage, however, is that a full backup takes longer to perform and requires a lot of storage space. Thus, full backups are typically run only periodically. Typically, backup operations employ a full backup in combination with either incremental or differential backups.
- Incremental backup: This type of backup involves backing up data created or changed since any last backup activity. This could be the most recent full backup or the last incremental backup. Backup applications track and record both date and time stamps of files to track assets modified since the last data backup to run an incremental backup. Since only the recent changes (increments) are backed up, it comes with less storage space and results in a quicker backup. Organisations can run incremental backups as often as desired, with only the most recent changes stored.
- Differential backup: A differential backup straddles the line between a full and an incremental backup. It involves backing up files, folders, and hard drives that were created or changed since the last full backup and subsequent incremental backups. To put it simply, a full backup is done initially, and then subsequent backups are run to include all the changes made to those files and folders (compared to just the changes since the last incremental backup). This will store more backed-up data than an incremental backup, but typically less than a full backup.
What’s the best backup data solution for businesses?
Businesses should use the 3-2-1 method of backup – this involves making three copies of your data, two local (on identical but separate hard drives) and one offsite in cloud storage. Choosing the right type of backup for your business will depend on the amount and type of data you need to back up. If your organisation deals in high volumes of data, you will need to use a combination of full and differential backups. This will include a unique system that backs up all of your domain, server, and network information both onsite and offsite, so you'll always be able to recover access to your data quickly.
Backup vulnerabilities
Hackers are increasingly looking at vulnerabilities in backup software and how they can infiltrate these systems through either backdoor attacks, inadequate security patching by the vendor, or by intercepting encryption keys to gain access to confidential data files. Businesses should check the security protocols (including user authentication, security updates, incident reporting, etc.) and the encryption infrastructure of their data backup providers.
Are online backups safe?
Yes, cloud backups (also known as online backup or remote backup) are relatively safe, likely much more so than hard drive storage. Most enterprises use more than one cloud storage solution, so it’s safe to say it’s perfectly secure and safe to use provided you’ve got a comprehensive cloud storage plan to mitigate risks of misconfigurations or data losses. Cloud storage is designed from the ground up for maximum data security. All data files in the cloud are encrypted and locked away to ward off cybercriminals. What’s more, data in the cloud is stored redundantly to ensure that business-critical information always exists somewhere and survives in any event. Cloud providers also continuously employ various security measures to protect business data, including built-in firewalls, third-party security testing, artificial intelligence (AI) and auto-patching, and backups, just to name a few.
Read more: What is cloud storage & is it safe?
Can cloud backup be hacked?
Cloud storage may be safer than traditional on-premise storage systems, but it’s not immune from cyber threats. The most common type of cyber attack on online backups is phishing which companies can easily mitigate. Most cloud storage providers including popular ones like Google Drive, Dropbox, OneDrive, and iCloud use HTTPS, as well as SSL encryption for all data, multi-factor authentication, and other security measures to safeguard their services.
Read more: What is encryption & how does it protect your data?
Where to start with data backups
Every business needs the right backup and disaster recovery plan for its operations and budget, and that’s where consulting a cyber security expert comes in. We can help you with a strategy that complements your existing infrastructure and protects your systems and data from any adverse events. Contact us via email: enquiries@xiphcyber.com.
Posted in: Security


