Published Jul 12, 2023 by Xiph
Suspicious network activity, malware attacks and cyber breaches typically leave digital red flags – or indicators of compromise (IOCs) − that can alert security teams of these security threats and help better coordinate incident response and disaster recovery.

What are indicators of compromise (IOCs)?
Indicators of compromise (IOCs) are forensic evidence or clues of potential intrusion into your organisation's network or system. Some include simple elements like metadata, log entries or files and others are more complex. These essential clues help IT teams better respond to a cyber attack. Indicators of compromise can discover cyber attacks and identify what malware/vectors were used in the breach, the IP addresses involved and other technical details. Information security professionals can recognise IOCs using expertise in their respective fields and advanced technology to scan large network traffic and isolate suspicious activities.
How do indicators of compromise (IOCs) work?
Indicators of compromise are early warning signs of malicious activity. These are gathered using threat intelligence, monitoring security logs, and analysing network traffic. The right cyber security stack can uncover unusual activities like strange network patterns, unexplained configuration changes or suspicious code typically indicating a potential or in-progress data breach or systems compromise.
For example, when a malware attack occurs, there are typically traces of malicious code left in the system or log files. These IOCs present the activity on your network that you wouldn’t otherwise see in real-time. Security teams will collect the IOC or ‘forensic data’ from these files for investigation if a security breach is identified.
Anti-malware software and other technologies use known indicators of compromise like virus signature to proactively guard against cyber threats. Indicators of compromise can also be used in anti-virus programs and heuristic analysis.
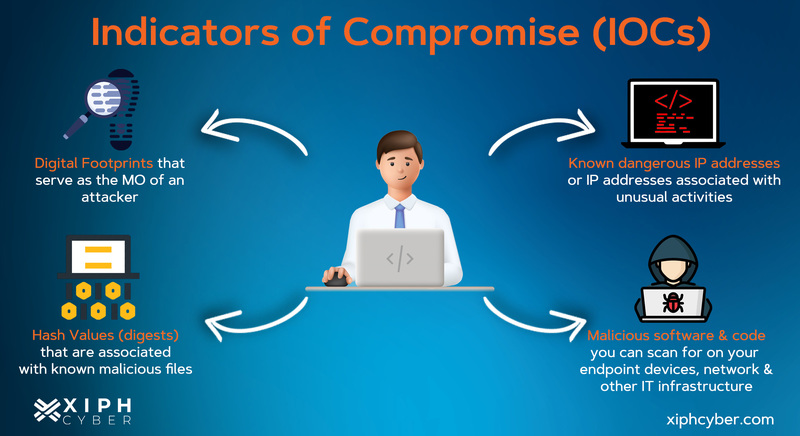
Types of indicators of compromise (IOCs)
Here are some common IOCs to watch out for:
Network IOCs: These may find suspicious activity on your network like unusual traffic patterns, connection to IP addresses and domains belonging to botnets or malware C&C servers, activity from strange geographic areas, unexpected protocols or ports being used, DNS request anomalies, etc. Network IOCs can be detected through various network monitoring tools, including intrusion detection systems (IDS) and security information and event management (SIEM) systems.
Host-based IOCs. These suggest suspicious activity on a specific computer or system such as unauthorised configuration changes to files, registers, or device settings. Host-based IOCs can be detected through endpoint security solutions.
File-based IOCs. These may indicate the presence of malicious files or malware on a system. These can include suspicious files, applications, and processes, or unexpected software or application updates. File-based IOCs can be detected through various file-scanning and sandboxing tools.
Behavioural IOCs: These show suspicious user activity on a network or system such as multiple login and authentication attempts that may indicate brute force attacks, suspicious activity in administrator or privileged accounts, many requests for the same file or unauthorised access to sensitive data. User monitoring tools can detect behavioural IOCs, including user and entity behaviour analytics (UEBA) solutions.
Indicators of compromise (IOCs) vs indicators of attack (IOAs): What’s the difference?
Indicators of compromise (IOCs) and indicators of attack (IOAs) work very much the same way with one major difference. Indicators of attack focus on identifying attacker activity while an attack is happening, whereas IOCs focus on examining what happened after an attack has occurred.
Why are indicators of compromise (IOCs) important?
Indicators of compromise (IOCs) help security teams detect and respond to cyber attacks more effectively. Organisations can monitor known IOCs to detect potential threats and spot malicious activity early in the attack sequence. Collecting and correlating IOCs in real time helps businesses quickly mitigate breaches and develop more effective incident response plans.
If security teams discover recurrence or patterns of specific IOCs, they can update their security tools and policies to protect against future attacks. IOCs can also be shared between organisations to pool resources and mitigate potential threats more effectively.
How to manage IOCs & best practices
Managing IOCs effectively requires a multipronged approach and some key security tools.
Identity and access management (IAM): Ensures you have robust identity and access management controls in place to identify who has access to what and detect any unusual activity.
Network segmentation: Dividing your network into smaller, distinct sub-networks can help limit the damage caused by a breach. Segments can have their own security policies and access controls.
Cyber threat intelligence: Use AI and machine learning to stay up to date with the rapidly evolving cyber threat landscape. This can help identify potential new threats and act before they materialise.
Dedicated IOC tools. Use firewalls, cyber security analytics, endpoint detection and response (EDR), penetration testing and network intrusion detection solutions to identify and manage IOCs effectively.
A final word
Indicators of compromise (IOCs) best practices encompass several techniques, including using automated tools, artificial intelligence (AI), and various algorithms to monitor, detect, and analyse evidence of cyber attacks. Regularly updating IOC procedures is important as new technologies and attack vectors emerge. For more information, contact us via email: enquiries@xiphcyber.com.
Posted in: Security


